Anchorage (Alaska) - geography.
Publié le 04/05/2013

Extrait du document
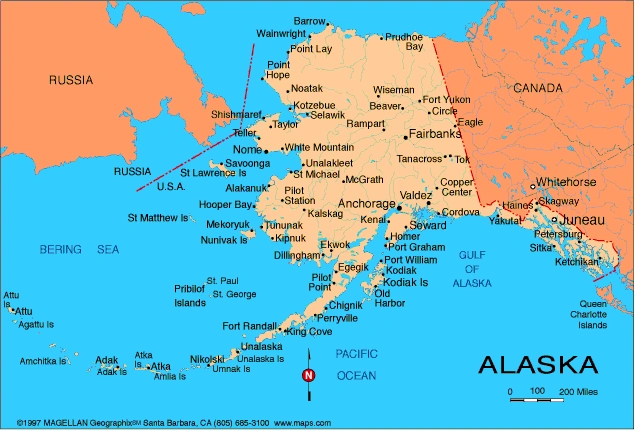
Anchorage (Alaska) - geography. Anchorage (Alaska), municipality in southern Alaska and a seaport on the Knik and Turnagain arms of Cook Inlet, at the base of the Chugach Mountains. Anchorage is the largest city in the state and serves as the transportation, commercial, and communications center for much of central and western Alaska. It is connected by Glenn Highway to the Alaska Highway, a road to Dawson Creek, British Columbia. It is also served by Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport, which is a major international hub for air freight. The city's economy is largely associated with Alaska's abundant natural resources, particularly petroleum, natural gas, and fish. Two nearby United States military bases built during World War II (1939-1945), Fort Richardson and Elmendorf Air Force Base, are important local employers. In addition, tourism has become a mainstay of the economy. A campus (established in 1954) of the University of Alaska and Alaska Pacific University (1959) are in Anchorage. Situated in an area of spectacular beauty, the opportunities in Anchorage for outdoor recreation are vast but the city also is home to a number of cultural institutions. Museums include the Anchorage Museum of History and Art; the Alaska Aviation Heritage Museum, which houses over 20 vintage aircraft dating from 1929 to 1944; and the Potter Section House Railroad Museum, in nearby Chugach State Park. The city is also the site of the Alaska Center for the Performing Arts, the Alaska Botanical Garden, and the Oscar Anderson House, a restored home built in 1915. Other places of interest include Portage Glacier, where huge ice blocks can be seen falling off the glacier's face into a lake below; Earthquake Park, where visitors can find depictions of the March 1964 earthquake that destroyed much of the city; and Eklutna Village Historical Park, with exhibits about the traditions and culture of the Native Americans and Russians who have lived in Anchorage for more than 350 years. Annual events include the Anchorage Fur Rendezvous, in February, commemorating the annual gathering in the past of trappers and miners, and the Anchorage to Nome Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, in March. The community was established in 1915 as the construction headquarters of the Alaska Railroad to Fairbanks. Anchorage incorporated in 1920, and engineers of the U.S. Army laid out the city in a grid during the decade. It grew rapidly during World War II, when it became the headquarters for the U.S. Alaska Defense Command. In 1942 the Alaska Highway was built as part of the defense of the West Coast, connecting the region to the rest of the country. A major earthquake on March 27, 1964, caused several deaths and extensive damage, but the city was rebuilt quickly. Anchorage experienced another boom in its economy in the late 1960s, when oil was discovered in Prudhoe Bay and other oil fields. The Alaska Pipeline, which is used to transport oil, was built in the mid-1970s. Anchorage covers a land area of 4,396 sq km (1,697 sq mi), with a mean elevation of 31 m (101 ft). According to the 2000 census, whites are 72.2 percent of the population, Native Americans 7.3 percent, blacks 5.8 percent, Asians 5.5 percent, and Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders 0.9 percent. The remainder are of mixed heritage or did not report race. Hispanics, who may be of any race, are 5.7 percent of the people. Population 174,431 (1980); 226,338 (1990); 260,283 (2000); 275,043 (2005 estimate). Microsoft ® Encarta ® 2009. © 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Liens utiles
- Anchorage (Alaska) - geography.
- Alaska - geography.
- Les êtres vivants et l'énergie Baleine à bosse bondissant hors de l'eau près des côtes d'Alaska, États-Unis.
- Les poilus d'Alaska
- Alaska - geographie.
