Map - geography.
Publié le 26/05/2013

Extrait du document
«
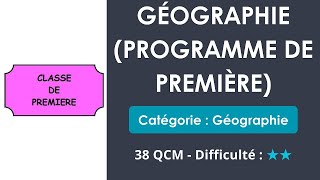
Relief MapRelief maps are three-dimensional models of the terrain in an area; on them, color and scale are used to indicate geographicalfeatures rather than simply to delineate political boundaries.
Because of this feature, relief maps are extensively used in engineeringand the military.
This map shows portions of Alaska and northwestern Canada.United States Geological Survey
Among the most important of the special-purpose maps are hydrographic and aviation charts.
Hydrographic charts are used for the navigation of ships and cover the surfaceof the oceans and other large bodies of water and their shores.
Over the water portion of a chart, depths are shown at frequent intervals by printing the number of fathomsof water at low tide.
Shoal areas are circled or shaded to give them greater visibility, and the limits of channels are shown by lines.
The type of bottom, such as sand, mud,or rock, is also indicated.
An important feature of such charts is the exact location of lighthouses, buoys, and other aids to navigation.
The only other shore features shownon a chart are such landmarks as tall buildings or prominent peaks on which a navigator may wish to take a bearing.
Aviation charts for use over land somewhat resembletopographic maps but bear in addition the location of radio beacons, airways, and the areas covered by the beams of radio range stations.
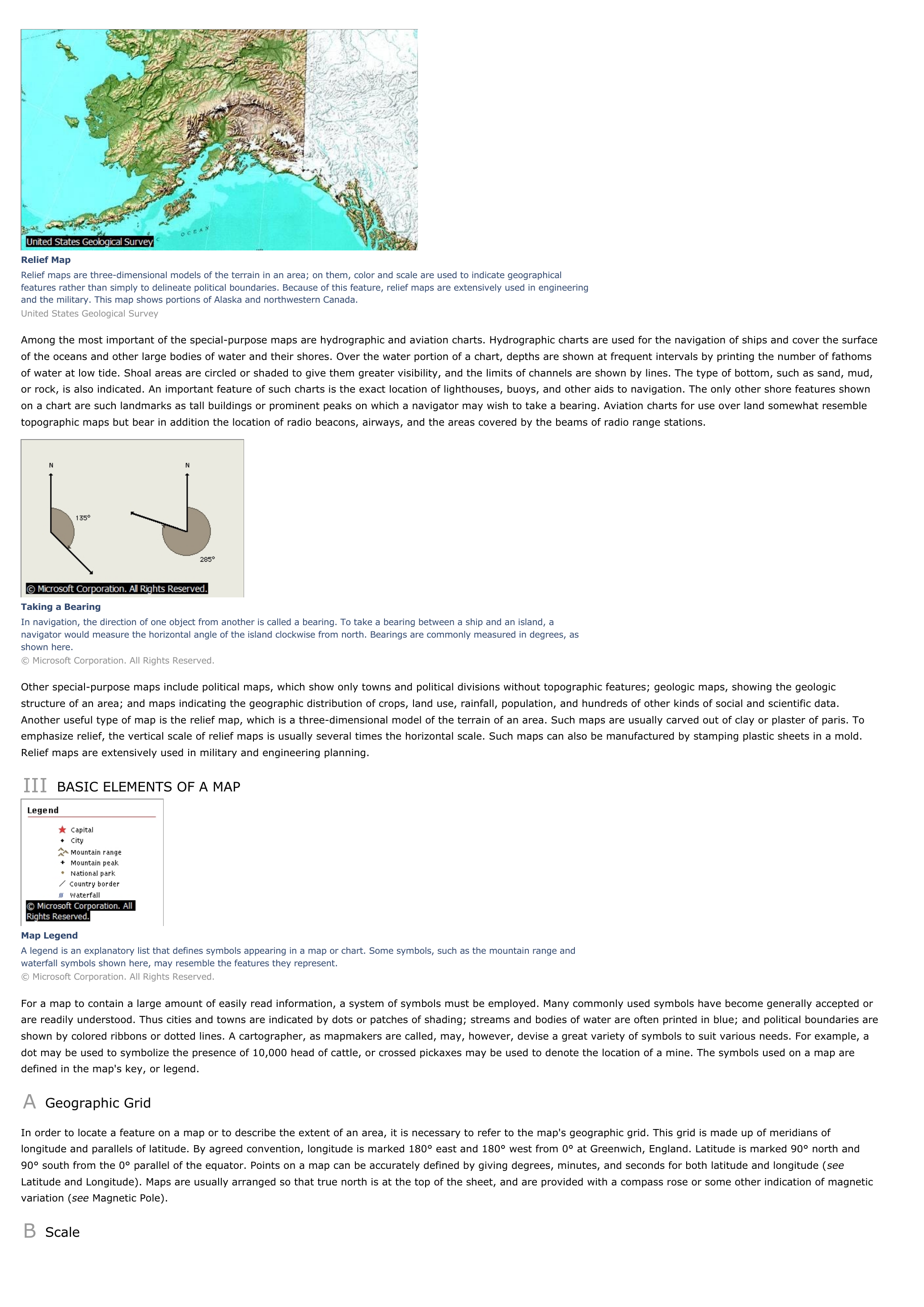
Taking a BearingIn navigation, the direction of one object from another is called a bearing.
To take a bearing between a ship and an island, anavigator would measure the horizontal angle of the island clockwise from north.
Bearings are commonly measured in degrees, asshown here.© Microsoft Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
Other special-purpose maps include political maps, which show only towns and political divisions without topographic features; geologic maps, showing the geologicstructure of an area; and maps indicating the geographic distribution of crops, land use, rainfall, population, and hundreds of other kinds of social and scientific data.Another useful type of map is the relief map, which is a three-dimensional model of the terrain of an area.
Such maps are usually carved out of clay or plaster of paris.
Toemphasize relief, the vertical scale of relief maps is usually several times the horizontal scale.
Such maps can also be manufactured by stamping plastic sheets in a mold.Relief maps are extensively used in military and engineering planning.
III BASIC ELEMENTS OF A MAP
Map LegendA legend is an explanatory list that defines symbols appearing in a map or chart.
Some symbols, such as the mountain range andwaterfall symbols shown here, may resemble the features they represent.© Microsoft Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
For a map to contain a large amount of easily read information, a system of symbols must be employed.
Many commonly used symbols have become generally accepted orare readily understood.
Thus cities and towns are indicated by dots or patches of shading; streams and bodies of water are often printed in blue; and political boundaries areshown by colored ribbons or dotted lines.
A cartographer, as mapmakers are called, may, however, devise a great variety of symbols to suit various needs.
For example, adot may be used to symbolize the presence of 10,000 head of cattle, or crossed pickaxes may be used to denote the location of a mine.
The symbols used on a map aredefined in the map's key, or legend.
A Geographic Grid
In order to locate a feature on a map or to describe the extent of an area, it is necessary to refer to the map's geographic grid.
This grid is made up of meridians oflongitude and parallels of latitude.
By agreed convention, longitude is marked 180° east and 180° west from 0° at Greenwich, England.
Latitude is marked 90° north and90° south from the 0° parallel of the equator.
Points on a map can be accurately defined by giving degrees, minutes, and seconds for both latitude and longitude ( see Latitude and Longitude).
Maps are usually arranged so that true north is at the top of the sheet, and are provided with a compass rose or some other indication of magneticvariation ( see Magnetic Pole).
B Scale.
»
↓↓↓ APERÇU DU DOCUMENT ↓↓↓
Liens utiles
- Map - Geography.
- MAP Bio
- Indian Art and Architecture I INTRODUCTION Art on the Indian Subcontinent This map highlights places in India and Pakistan where prominent examples of Indian art and architecture have been produced.
- Tokyo - geography.
- Toronto - geography.