Winnipeg - geography.
Publié le 26/05/2013

Extrait du document
«
city of the province.
The city is also the site of the University of Winnipeg.Tom McHugh/Photo Researchers, Inc.
Winnipeg grew up around the district called The Forks, at the river junction.
For many years this historic site was covered by railroad yards, but in recent years it has beenredeveloped as a heritage park and recreation center.
Winnipeg also has an impressive collection of pre-1914 buildings, especially in the Exchange District, with itswarehouses and office blocks.
Old Market Square, a popular downtown park, is located in the Exchange District too.
Close by is Centennial Centre, a modern complex, whichis home to three of Canada’s leading arts organizations, the Royal Winnipeg Ballet, the Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra, and the Manitoba Opera.
Adding to Winnipeg’s richcultural scene are a number of other musical and theatrical groups, including the Manitoba Theatre Company.
Of the city’s various annual festivals, the New Music Festival,the Folk Festival, and Folklorama (a celebration of Winnipeg’s many ethnic groups) are probably the best known.
Important institutions in Winnipeg include the University ofManitoba (1877), the University of Winnipeg (1967), the Winnipeg Art Gallery, and the Museum of Man and Nature.
The city also has a number of specialized museums.
Winnipeg’s best-known sports team, the Blue Bombers of the Canadian Football League (CFL), plays in Canad Inns Stadium.
The Manitoba Moose of the InternationalHockey League are based close by, at Winnipeg Arena.
Winnipeg has many parks and recreational facilities, especially along the Assiniboine.
The largest, Assiniboine Park,offers various attractions, including a zoo and a sculpture garden.
The grounds of the Manitoba Legislative Building also open onto the Assiniboine.
IV ECONOMY
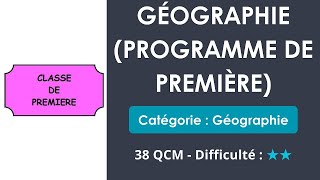
Pacific Rail Yards, WinnipegThe city of Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, began as a railroad center, and railroading continues to form an important part of theeconomy.
The city is a major junction for rail traffic into Canada’s prairie region from the east.Porterfield/Chickering/Photo Researchers, Inc.
Winnipeg has a diversified economy.
The prairie soils are fertile and produce large quantities of grain and livestock.
The area north and east of the city is rich in forest andmineral resources and water power for electricity.
In addition to providing public services of all kinds, Winnipeg is the distribution center for the eastern prairies and thenorthwestern province of Ontario and a financial and grain marketing center.
It has a broad industrial base, with industries involved in the manufacture and repair ofagricultural and transportation equipment, brewing, meatpacking, clothing and textiles, and medical research.
The city is also home to the headquarters and mainproduction facility of the Royal Canadian Mint.
Because of its strategic location, Winnipeg serves as the transportation gateway to the prairie region from the east.
The city is located on both of Canada’s transcontinentalrailways—the Canadian National and the Canadian Pacific—and the Trans-Canada Highway.
It also has a busy international airport.
V GOVERNMENT
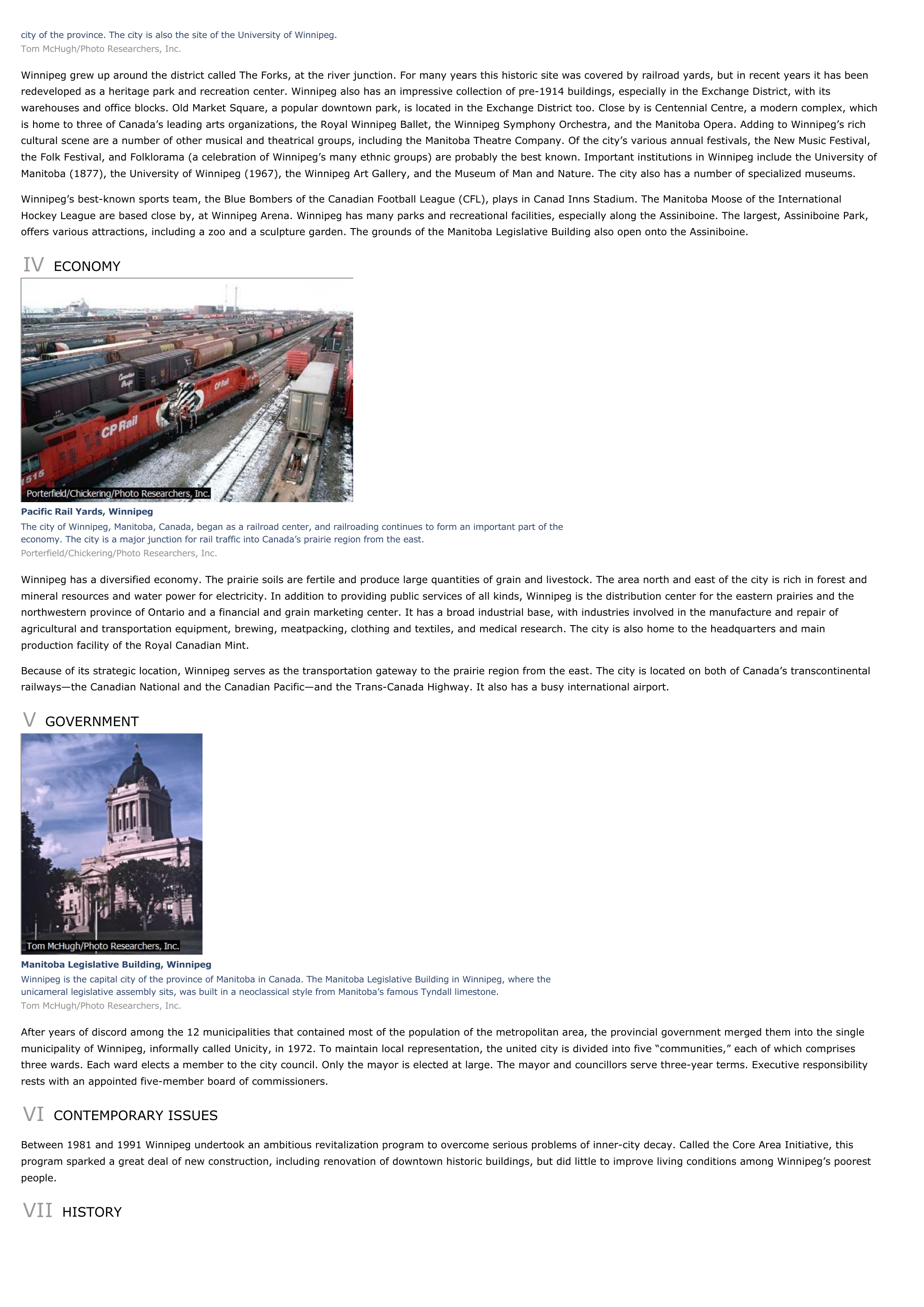
Manitoba Legislative Building, WinnipegWinnipeg is the capital city of the province of Manitoba in Canada.
The Manitoba Legislative Building in Winnipeg, where theunicameral legislative assembly sits, was built in a neoclassical style from Manitoba’s famous Tyndall limestone.Tom McHugh/Photo Researchers, Inc.
After years of discord among the 12 municipalities that contained most of the population of the metropolitan area, the provincial government merged them into the singlemunicipality of Winnipeg, informally called Unicity, in 1972.
To maintain local representation, the united city is divided into five “communities,” each of which comprisesthree wards.
Each ward elects a member to the city council.
Only the mayor is elected at large.
The mayor and councillors serve three-year terms.
Executive responsibilityrests with an appointed five-member board of commissioners.
VI CONTEMPORARY ISSUES
Between 1981 and 1991 Winnipeg undertook an ambitious revitalization program to overcome serious problems of inner-city decay.
Called the Core Area Initiative, thisprogram sparked a great deal of new construction, including renovation of downtown historic buildings, but did little to improve living conditions among Winnipeg’s poorestpeople.
VII HISTORY.
»
↓↓↓ APERÇU DU DOCUMENT ↓↓↓
Liens utiles
- Winnipeg - Geography.
- Stanley Cup Winners Year Champion 1893 Montréal AAA 1894 Montréal AAA 1895 Montréal Victorias 1896 Winnipeg Victorias 1897-98 Montréal Victorias 1899 Feb.
- Tokyo - geography.
- Toronto - geography.
- Venice (Italy) - geography.